
White-label shop for digital intelligent assistance and human-AI collaboration in manufacturing
THE PROJECT
WASABI focuses on digital intelligent assistance solutions, based on human-AI collaboration, and applied to the manufacturing domain. The WASABI solution increases the cognitive abilities of workers and accelerates the acquisition and transfer of knowledge, through Natural Language Processing (NLP) system, for the upskilling of the existing workforce, meantime securing job positions.
Our challenge is related to SMEs and mid-caps manufacturers in Europe that need to meet sustainability goals. Producing components for complex products, or often operating in emerging specialty equipment markets, they must be quite careful about spending their resources on activities with uncertain costs or outcomes.
Wasabi makes digital intelligence assistance and conversational artificial intelligence solutions become standard practices, accessible, affordable, and manageable even for small companies. Wasabi allows European SMEs to achieve sustainability principles and technological and operational innovation capacity, such as to become renewed and cutting-edge, and reach leadership goals and market competitiveness.
TECHNOLOGY
WASABI reuses and customizes technologies from previous projects. The rEUse waste management digital platform, to manage circular economy information about circular entities, processes and services (SYXIS), that covers production and recycling, and COALA (BIBA, ICCS, and SYXIS), a human-centred AI-based digital assistant, focused on education and training, that covers production and product end-of-line testing. WASABI positions its business cases along the product life cycle to demonstrate its solution’s coverage and adaptability.
The three initial cases represent typical problems in manufacturing. The first business case concerns the valorisation of production waste. The second business case concerns the fast and cost-efficient onboarding of new factory workers. It combines knowledge management and learning theories with digital assistant technology. The third business case focuses on improving manufacturing quality. It covers, for instance, product tests and end-of-line quality control procedures and applies digital assistant technology in combination with prescriptive quality analytics.
TECHNOLOGY
WASABI reuses and customises technologies from previous projects. The rEUse waste management digital platform, to manage circular economy information about circular entities, processes and services (SYXIS), that covers production and recycling, and COALA (BIBA, ICCS, and SYXIS), a human-centred AI-based digital assistant, focused on education and training, that covers production and product end-of-line testing. WASABI positions its business cases along the product life cycle to demonstrate the coverage and adaptability of its solution.
The three initial cases represent typical problems in manufacturing. The first business case concerns the valorisation of production waste. The second business case concerns the fast and cost-efficient onboarding of new factory workers. It combines knowledge management and learning theories with digital assistant technology. The third business case focuses on improving manufacturing quality. It covers, for instance, product tests and end-of-line quality control procedures and applies digital assistant technology in combination with prescriptive quality analytics.
GOALS
01
Sustainability
Aims at minimising the number of sustainability incidents in manufacturing, through the implementation of DIA (Digital Intelligent Assistant) solutions. It focuses on waste valorisation and product quality test procedures optimisation, to save energy and materials.
02
Agility & Resilience
Aims at reducing the training time for workers in manufacturing. It focuses on assisted workforce management to shorten the onboarding of new workers, and to optimise the upskill of other roles, providing a training concept and materials for human-AI collaboration.
03
Technology Adoption
Aims at increasing the uptake of intelligent digital assistance technology, to augment workers’ cognitive capabilities, assist them during difficult tasks, guiding them through knowledge-intensive procedures where lapses could result in injury, and allowing them to delegate the simpler activities.
04
Innovation capacity
Aims at making digital assistance technologies and related services available to innovation infrastructures. It focuses on providing an overview about Europe’s legal framework regarding AI related contract law and the emerging trustworthy AI legislation, increasing innovation capacity, agility and productivity of the manufacturing sector, in particular for SMEs and mid-caps.
05
Leadership
Aims at overcoming barriers and scepticism about intelligent digital assistance in industry. It focuses on increasing competitiveness through customised e-commerce software with federation capabilities and a cloud and edge deployment for DIA infrastructure, contributing to standardization on conversational AI and interoperability.
USE CASE 1
Augmented waste management and valorisation
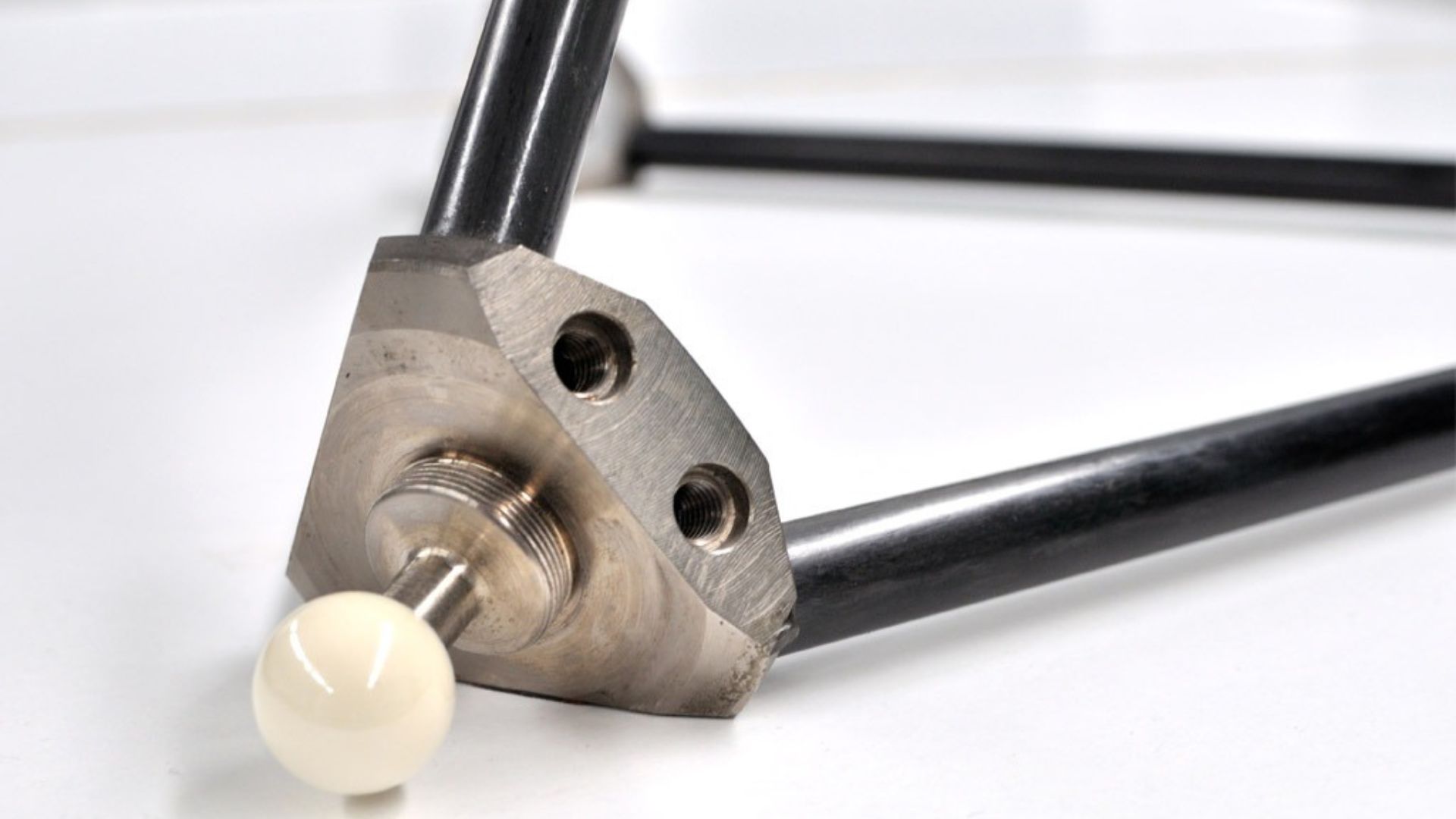

Image Credits: Trimek
Waste management for the manufacturing sector, through a conversational interface and rich-media records, to identify waste and determine if it qualifies for reuse.
This use case connects the COALA solution for cognitive assistance consisting of a composition of trustworthy AI components with a voice-enabled digital intelligent assistant as an interface, with the rEUse waste management platform.
In dimensional metrology, TRIMEK has developed a Digital Assistant that supports the operator in registering and consulting all relevant data related to calibration processes performed on calibration artifacts (tetrahedron, bar balls, cube). This data is automatically stored in the rEUse platform, where it can also be accessed for consultation. BIBA and SYXIS collaborate in developing these solutions as technology providers. The solution is delivered, tested, improved, validated, and installed at TRIMEK’s premises. It is currently in the phase of assessing the project KPIs.
In recycling and revamping, surgical tools provider CROMA uses the assistant during post-surgery quality control in the central sterilization unit. The assistant helps classify instruments that do not meet quality standards, identifying whether they can be repaired or need replacement. All data is stored in the rEUse database, enabling continuous monitoring, traceability, and supporting a circular economy approach by facilitating recycling and recovery of surgical instruments.
USE CASE 2
Assisted workforce management
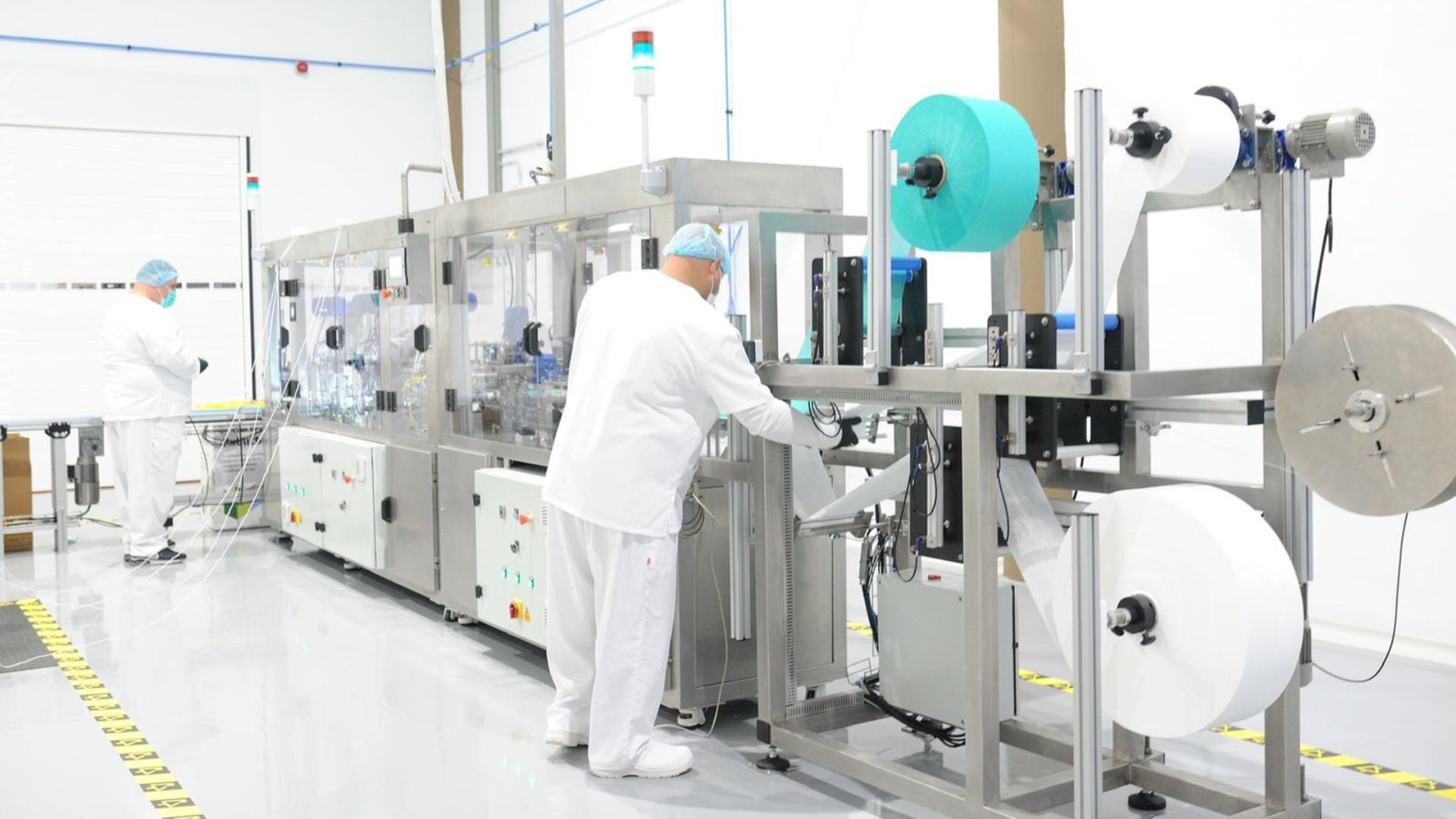

Image Credits: EPSICAN
Manufacturing workforce management towards the use of human-centred AI-based digital assistance solutions to onboard and integrate new workers facing different job experience, education, ethnic, social and demographic background, and language issues.
This use case aims to increase agility by rapidly upskilling the workforce of the organisation.
WASABI demonstrates its solution in this use case by customising the COALA assistant’s dialog model and creating a knowledge base that captures what new workers should focus on during the onboarding process.
EPISCAN strengthens worker integration and participation by using an onboarding assistant to train new staff on machinery handling and cleanroom protocols, improving the learning curve and supporting more consistent adoption of procedures across diverse teams, including foreign employees.
USE CASE 3
Assisted quality assurance for sustainable products
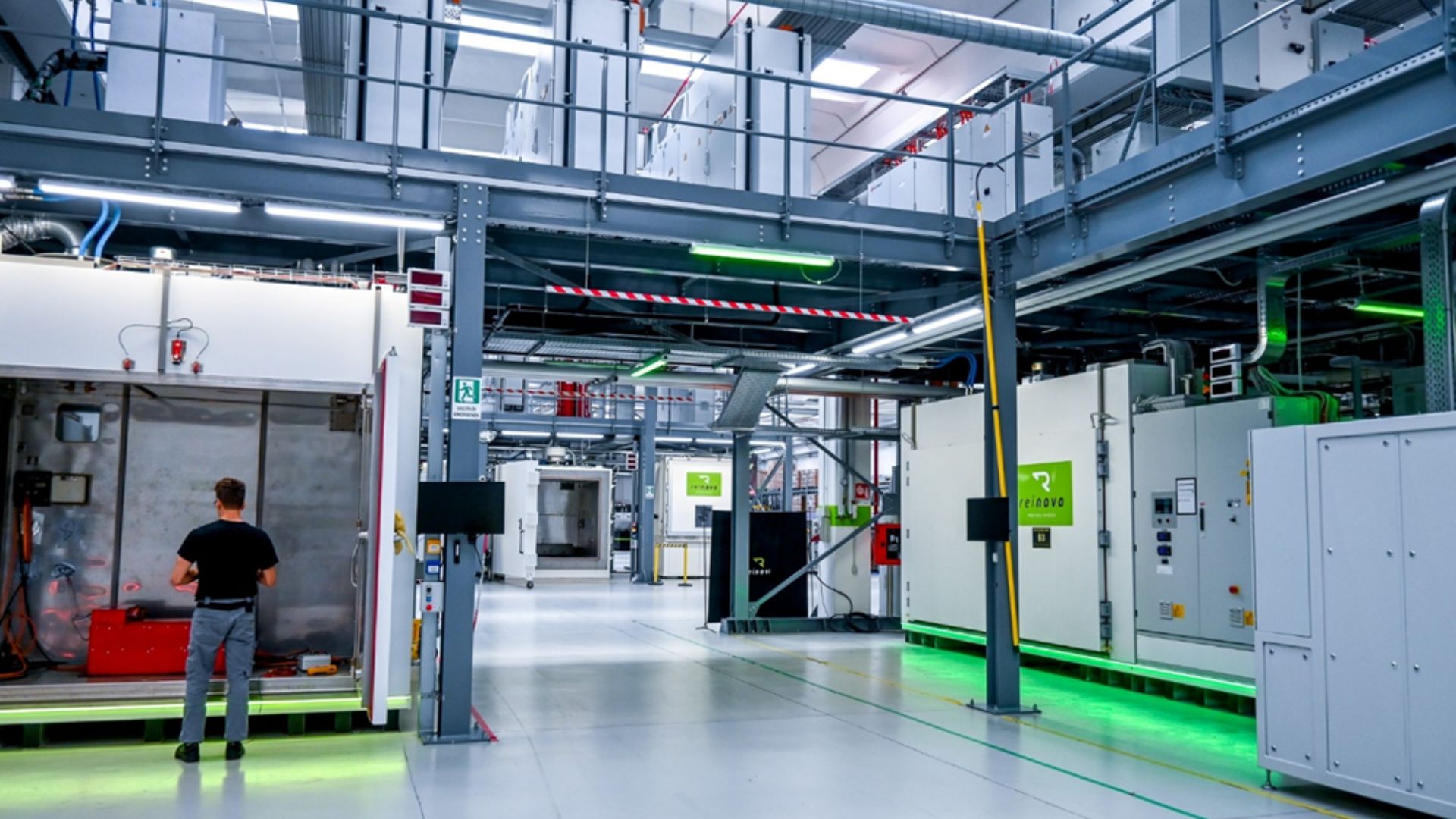

Image Credits: Reinova
Augmentation of product quality testing to increase product and worker safety, reduce carbon footprint, strengthen workers’ cognitive skills, and reduce the burden of repetitive, error-prone, and knowledge-intensive activities.
Assisted quality assurance for sustainable products.
WASABI demonstrates its solution in five cases with target users. REINOVA has deployed a first test version of an AI-based chatbot that monitors laboratory testing equipment, especially climatic chambers; operators use it via mobile devices to check machine status, verify ongoing tests, and identify anomalies, improving laboratory efficiency while supporting reduced downtime, lower energy consumption, and safer and more reliable testing environments. TRIMEK uses an assistant developed by UNIMORE to support Coordinate Measuring Machine operators during alignment activities in M3 Metrology: the assistant helps select the correct project template for the specific artifact being measured (tetrahedron, bar ball, cube) and guides the operator through the required alignment steps; after an initial experimental use, the assistant is in an improvement phase with additional features being integrated, and a second evaluation phase is planned based on questionnaires completed by defined champions and additional operators. EPISCAN has integrated voice-controlled quality checks on the mask production line, enabling hands-free operation; Phase 2 testing of the AQA assistant is being finalised with a focus on the Prevention module and safety protocols, and an onboarding assistant is already used to train new staff on machinery handling and cleanroom protocols, improving the learning curve. CROMA uses the Quality Assistant during the packaging phase of surgical instrument kits prior to sterilisation: the assistant supports checking and counting instruments against the kit lists, minimising non-value-added manual tasks, improving process efficiency, and strengthening safety and reliability as perceived by surgeons and patients. KLISBIO will introduce the assistant to support the workforce in the production of silk-based prosthetics
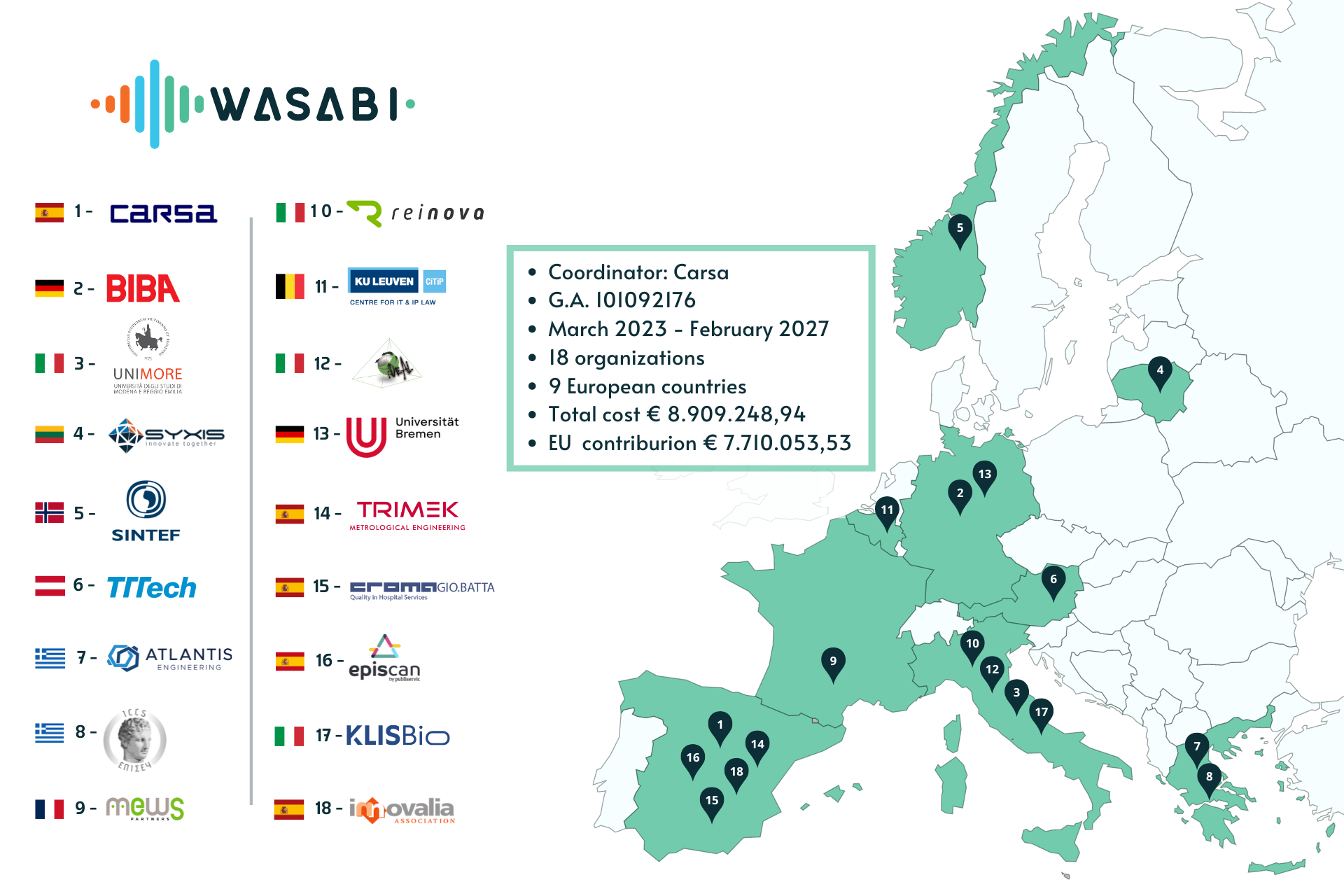
OUR NUMBERS
A strong consortium has been built to cover all aspects of technical, industrial, and business requirements, going from industry to academia, to provide a complete value chain to bring new products and services to the manufacturing market.


